Abstract
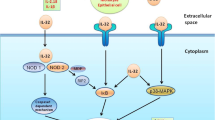
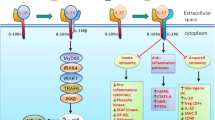
Interleukin-33 (IL-33) belongs to the IL-1 cytokine family and plays an important role in modulating immune system by inducing Th2 immune response via the ST2 membrane receptor. Epithelial cells are the major producers of IL-33. However, IL-33 is also secreted by other cells, e.g., bone marrow cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, and mast cells. IL-33 targets a broad range of cell types bearing the ST2 surface receptor. Many ST2-positive cells, such as Th2 cells, mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils, are involved in the development of allergic bronchial asthma (BA). This suggests that IL-33 directly participates in BA pathogenesis. Currently, the role of IL-33 in pathogenesis of inflammatory disorders, including BA, has been extensively investigated using clinical samples collected from patients, as well as asthma animal models. In particular, numerous studies on blocking IL-33 and its receptor by monoclonal antibodies in asthma mouse model have been performed over the last several years; IL-33-and ST2-deficient transgenic mice have also been generated. In this review, we summarized and analyzed the data on the role of IL-33 in BA pathogenesis and the prospects for creating new treatments for BA.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a.a.:
-
amino acid residue
- BA:
-
bronchial asthma
- BAL:
-
bronchoalveolar lavage
- bp:
-
base pair
- Ig:
-
immunoglobulin
- IL:
-
interleukin
References
Onda, H., Kasuya, H., Takakura, K., Hori, T., Imaizumi, T., Takeuchi, T., Inoue, I., and Takeda, J. (1999) Identification of genes differentially expressed in canine vasospastic cerebral arteries after subarachnoid hemorRhage, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 19, 1279–1288.
Baekkevold, E. S., Roussigne, M., Yamanaka, T., Johansen, F.-E., Jahnsen, F. L., Amalric, F., Brandtzaeg, P., Erard, M., Haraldsen, G., and Girard, J.-P. (2003) Molecular characterization of NF-HEV, a nuclear factor preferentially expressed in human high endothelial venules, Am. J. Pathol., 163, 69–79.
Schmitz, J., Owyang, A., Oldham, E., Song, Y., Murphy, E., McClanahan, T. K., Zurawski, G., Moshrefi, M., Qin, J., Li, X., Gorman, D. M., and Bazan, J. F. (2005) IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines, Immunity, 23, 479–490.
Sims, J. E., Pan, Y., Smith, D. E., Nicklin, M. J. H., Barton, J. L., Bazan, J. F., Kastelein, R. A., Busfield, S. J., Ford, J. E., Lin, H., Mulero, J. J., Kumar, S., Pan, J., and Young, P. R. (2001) A new nomenclature for IL-1-family genes, Trends Immunol., 22, 536–537.
Dinarello, C., Arend, W., Sims, J., Smith, D., Blumberg, H., O’Neill, L., Goldbach-Mansky, R., Pizarro, T., Hoffman, H., Bufler, P., Nold, M., Ghezzi, P., Mantovani, A., Garlanda, C., Boraschi, D., Rubartelli, A., Netea, M., van der Meer, J., Joosten, L., Mandrup-Poulsen, T., Donath, M., Lewis, E., Pfeilschifter, J., Martin, M., Kracht, M., Muehl, H., Novick, D., Lukic, M., Conti, B., Solinger, A., Kelk, P., Peyman, K., van de Veerdonk, F., and Gabel, C. (2010) IL-1 family nomenclature, Nat. Immunol., 11, 973.
Lingel, A., Weiss, T. M., Niebuhr, M., Pan, B., Appleton, B. A., Wiesmann, C., and Bazan, J. F. (2009) Structure of IL-33 and its interaction with the ST2 and IL-1 RAcP receptors–insight into heterotrimeric IL-1 signaling complexes, Structure, 17, 1398–1410.
Liu, X., Hammel, M., He, Y., Tainer, J. A., Jeng, U. S., Zhang, L., Wang, S., and Wang, X. (2013) Structural insights into the interaction of IL-33 with its receptors, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 110, 14918–14923.
Arend, W. P., Palmer, G., and Gabay, C. (2008) IL-1, IL-18, and IL-33 families of cytokines, Immunol. Rev., 223, 20–38.
Barksby, H. E., Lea, S. R., Preshaw, P. M., and Taylor, J. J. (2007) The expanding family of interleukin-1 cytokines and their role in destructive inflammatory disorders, Clin. Exp. Immunol., 149, 217–225.
Dinarello, C. A. (1994) The biological properties of interleukin-1, Eur. Cytokine Netw., 5, 517–531.
Dinarello, C. A. (2009) Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family, Annu. Rev. Immunol., 27, 519–550.
Thornberry, N. A., Bull, H. G., Calaycay, J. R., Chapman, K. T., Howard, A. D., Kostura, M. J., Miller, D. K., Molineaux, S. M., Weidner, J. R., and Aunins, J. (1992) A novel heterodimeric cysteine protease is required for interleukin-1β processing in monocytes, Nature, 356, 768–774.
Cayrol, C., and Girard, J.-P. (2009) The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is inactivated after maturation by caspase-1, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 106, 9021–9026.
Luthi, A. U., Cullen, S. P., McNeela, E. A., Duriez, P. J., Afonina, I. S., Sheridan, C., Brumatti, G., Taylor, R. C., Kersse, K., Vandenabeele, P., Lavelle, E. C., and Martin, S. J. (2009) Suppression of interleukin-33 bioactivity through proteolysis by apoptotic caspases, Immunity, 31, 84–98.
Kakkar, R., Hei, H., Dobner, S., and Lee, R. T. (2012) Interleukin 33 as a mechanically responsive cytokine secreted by living cells, J. Biol. Chem., 287, 6941–6948.
Carriere, V., Roussel, L., Ortega, N., Lacorre, D.-A., Americh, L., Aguilar, L., Bouche, G., and Girard, J.-P. (2007) IL-33, the IL-1-like cytokine ligand for ST2 receptor, is a chromatin-associated nuclear factor in vivo, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 104, 282–287.
Hayakawa, M., Hayakawa, H., Matsuyama, Y., Tamemoto, H., Okazaki, H., and Tominaga, S. (2009) Mature interleukin-33 is produced by calpain-mediated cleavage in vivo, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 387, 218–222.
Lefrancais, E., Roga, S., Gautier, V., Gonzalez-de-Peredo, A., Monsarrat, B., Girard, J. P., and Cayrol, C. (2012) IL-33 is processed into mature bioactive forms by neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 109, 1673–1678.
Dunne, A., and O’Neill, L. A. (2003) The interleukin-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: signal transduction during inflammation and host defense, Sci. STKE, re3.
Chackerian, A. A., Oldham, E. R., Murphy, E. E., Schmitz, J., Pflanz, S., and Kastelein, R. A. (2007) IL-1 receptor accessory protein and ST2 comprise the IL-33 receptor complex, J. Immunol., 179, 2551–2555.
Kakkar, R., and Lee, R. T. (2008) The IL-33/ST2 pathway: therapeutic target and novel biomarker, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov., 7, 827–840.
Lloyd, C. M. (2010) IL-33 family members and asthma–bridging innate and adaptive immune responses, Curr. Opin. Immunol., 22, 800–806.
Oboki, K., Ohno, T., Kajiwara, N., Saito, H., and Nakae, S. (2010) IL-33 and IL-33 receptors in host defense and diseases, Allergol. Int., 59, 143–160.
Miller, A. M. (2011) Role of IL-33 in inflammation and disease, J. Inflamm. (Lond.), 8, 22.
Iikura, M., Suto, H., Kajiwara, N., Oboki, K., Ohno, T., Okayama, Y., Saito, H., Galli, S. J., and Nakae, S. (2007) IL-33 can promote survival, adhesion and cytokine production in human mast cells, Lab. Invest., 87, 971–978.
Hudson, C. A., Christophi, G. P., Gruber, R. C., Wilmore, J. R., Lawrence, D. A., and Massa, P. T. (2008) Induction of IL-33 expression and activity in central nervous system glia, J. Leukoc. Biol., 84, 631–643.
Ohno, T., Oboki, K., Morita, H., Kajiwara, N., Arae, K., Tanaka, S., Ikeda, M., Iikura, M., Akiyama, T., Inoue, J., Matsumoto, K., Sudo, K., Azuma, M., Okumura, K., Kamradt, T., Saito, H., and Nakae, S. (2011) Paracrine IL-33 stimulation enhances lipopolysaccharide-mediated macrophage activation, PLoS One, 6, e18404.
Hayakawa, H., Hayakawa, M., Kume, A., and Tominaga, S. I. (2007) Soluble ST2 blocks interleukin-33 signaling in allergic airway inflammation, J. Biol. Chem., 282, 26369–26380.
Palmer, G., Talabot-Ayer, D., Lamacchia, C., Toy, D., Seemayer, C. A., Viatte, S., Finckh, A., Smith, D. E., and Gabay, C. (2009) Inhibition of interleukin-33 signaling attenuates the severity of experimental arthritis, Arthritis Rheum., 60, 738–749.
Pushparaj, P. N., Tay, H. K., H’ng, S. C., Pitman, N., Xu, D., McKenzie, A., Liew, F. Y., and Melendez, A. J. (2009) The cytokine interleukin-33 mediates anaphylactic shock, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 106, 9773–9778.
Bartunek, J., Delrue, L., Van Durme, F., Muller, O., Casselman, F., De Wiest, B., Croes, R., Verstreken, S., Goethals, M., De Raedt, H., Sarma, J., Joseph, L., Vanderheyden, M., and Weinberg, E. O. (2008) Nonmyocardial production of ST2 protein in human hypertrophy and failure is related to diastolic load, J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 52, 2166–2174.
Chapuis, J., Hot, D., Hansmannel, F., Kerdraon, O., Ferreira, S., Hubans, C., Maurage, C. A., Huot, L., Bensemain, F., Laumet, G., Ayral, A. M., Fievet, N., Hauw, J. J., DeKosky, S. T., Lemoine, Y., Iwatsubo, T., Wavrant-Devrieze, F., Dartigues, J. F., Tzourio, C., Buee, L., Pasquier, F., Berr, C., Mann, D., Lendon, C., Alperovitch, A., Kamboh, M. I., Amouyel, P., and Lambert, J. C. (2009) Transcriptomic and genetic studies identify IL-33 as a candidate gene for Alzheimer’s disease, Mol. Psychiatry, 14, 1004–1016.
Kurowska-Stolarska, M., Kewin, P., Murphy, G., Russo, R. C., Stolarski, B., Garcia, C. C., Komai-Koma, M., Pitman, N., Li, Y., Niedbala, W., McKenzie, A. N., Teixeira, M. M., Liew, F. Y., and Xu, D. (2008) IL-33 induces antigen-specific IL-5+ T cells and promotes aller-gic-induced airway inflammation independent of IL-4, J. Immunol., 181, 4780–4790.
Prefontaine, D., Lajoie-Kadoch, S., Foley, S., Audusseau, S., Olivenstein, R., Halayko, A. J., Lemiere, C., Martin, J. G., and Hamid, Q. (2009) Increased expression of IL-33 in severe asthma: evidence of expression by airway smooth muscle cells, J. Immunol., 183, 5094–5103.
Piedimonte, G. (2013) Respiratory syncytial virus and asthma: speed-dating or long-term relationship? Curr. Opin. Pediatr., 25, 344–349.
Thomsen, S. F., van der Sluis, S., Stensballe, L. G., Posthuma, D., Skytthe, A., Kyvik, K. O., Backer, V., and Bisgaard, H. (2009) Exploring the association between severe respiratory syncytial virus infection and asthma, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med., 179, 1091–1097.
Jackson, D. J., Makrinioti, H., Rana, B. M., Shamji, B. W., Trujillo-Torralbo, M. B., Footitt, J., Jerico, Del-Rosario, Telcian, A. G., Nikonova, A., Zhu, J., Aniscenko, J., Gogsadze, L., Bakhsoliani, E., Traub, S., Dhariwal, J., Porter, J., Hunt, D., Hunt, T., Hunt, T., Stanciu, L. A., Khaitov, M., Bartlett, N. W., Edwards, M. R., Kon, O. M., Mallia, P., Papadopoulos, N. G., Akdis, C. A., Westwick, J., Edwards, M. J., Cousins, D. J., Walton, R. P., and Johnston, S. L. (2014) IL-33-dependent type 2 inflammation during rhinovirus-induced asthma exacerbations in vivo, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med., 190, 1373–1382.
Hsu, C. L., Neilsen, C. V., and Bryce, P. J. (2010) IL-33 is produced by mast cells and regulates IgE-dependent inflammation, PLoS One, 5, e11944.
Ngoc, P. L., Gold, D. R., Tzianabos, A. O., Weiss, S. T., and Celedon, J. C. (2005) Cytokines, allergy, and asthma, Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 5, 161–166.
Shilovskiy, I. P., Eroshkina, D. V., Babakhin, A. A., and Khaitov, M. R. (2017) Anticytokine therapy of allergic asthma, Mol. Biol., 51, 1–13.
Lohning, M., Stroehmann, A., Coyle, A. J., Grogan, J. L., Lin, S., Gutierrez-Ramos, J. C., Levinson, D., Radbruch, A., and Kamradt, T. (1998) T1/ST2 is preferentially expressed on murine Th2 cells, independent of interleukin 4, interleukin 5, and interleukin 10, and important for Th2 effector function, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 6930–6935.
Nakae, S., Iwakura, Y., Suto, H., and Galli, S. J. (2007) Phenotypic differences between Th1 and Th17 cells and negative regulation of Th1 cell differentiation by IL-17, J. Leukoc. Biol., 81, 1258–1268.
Hoshino, K., Kashiwamura, S., Kuribayashi, K., Kodama, T., Tsujimura, T., Nakanishi, K., Matsuyama, T., Takeda, K., and Akira, S. (1999) The absence of interleukin 1 receptor-related T1/ST2 does not affect T helper cell type 2 development and its effector function, J. Exp. Med., 190, 1541–1548.
Townsend, M. J., Fallon, P. G., Matthews, D. J., Jolin, H. E., and McKenzie, A. N. (2000) T1/ST2-deficient mice demonstrate the importance of T1/ST2 in developing primary T helper cell type 2 responses, J. Exp. Med., 191, 1069–1076.
Smithgall, M. D., Comeau, M. R., Yoon, B. R., Kaufman, D., Armitage, R., and Smith, D. E. (2008) IL-33 amplifies both Th1-and Th2-type responses through its activity on human basophils, allergen-reactive Th2 cells, iNKT and NK cells, Int. Immunol., 20, 1019–1030.
Moulin, D., Donze, O., Talabot-Ayer, D., Mezin, F., Palmer, G., and Gabay, C. (2007) Interleukin (IL)-33 induces the release of pro-inflammatory mediators by mast cells, Cytokine, 40, 216–225.
Allakhverdi, Z., Comeau, M. R., Smith, D. E., Toy, D., Endam, L. M., Desrosiers, M., Liu, Y. J., Howie, K. J., Denburg, J. A., Gauvreau, G. M., and Delespesse, G. (2009) CD34+ hemopoietic progenitor cells are potent effectors of allergic inflammation, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 123, 472–478.
Silver, M. R., Margulis, A., Wood, N., Goldman, S. J., Kasaian, M., and Chaudhary, D. (2010) IL-33 synergizes with IgE-dependent and IgE-independent agents to promote mast cell and basophil activation, Inflamm. Res., 59, 207–218.
Suzukawa, M., Iikura, M., Koketsu, R., Nagase, H., Tamura, C., Komiya, A., Nakae, S., Matsushima, K., Ohta, K., Yamamoto, K., and Yamaguchi, M. (2008) An IL-1 cytokine member, IL-33, induces human basophil activation via its ST2 receptor, J. Immunol., 181, 5981–5989.
Pelaia, G., Vatrella, A., Busceti, M. T., Gallelli, L., Calabrese, C., Terracciano, R., and Maselli, R. (2015) Cellular mechanisms underlying eosinophilic and neutrophilic airway inflammation in asthma, Mediators Inflamm., 2015, 879783.
Cherry, W. B., Yoon, J., Bartemes, K. R., Iijima, K., and Kita, H. (2008) A novel IL-1 family cytokine, IL-33, potently activates human eosinophils, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 121, 1484–1490.
Dyer, K. D., Percopo, C. M., and Rosenberg, H. F. (2013) IL-33 promotes eosinophilia in vivo and antagonizes IL-5-dependent eosinophil hematopoiesis ex vivo, Immunol. Lett., 150, 41–47.
Besnard, A. G., Togbe, D., Guillou, N., Erard, F., Quesniaux, V., and Ryffel, B. (2011) IL-33-activated den-dritic cells are critical for allergic airway inflammation, Eur. J. Immunol., 41, 1675–1686.
Rank, M. A., Kobayashi, T., Kozaki, H., Bartemes, K. R., Squillace, D. L., and Kita, H. (2009) IL-33-activated den-dritic cells induce an atypical TH2-type response, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 123, 1047–1054.
Martin, F., and Kearney, J. F. (2000) B-cell subsets and the mature preimmune repertoire. Marginal zone and B1 B cells as part of a “natural immune memory”, Immunol. Rev., 175, 70–79.
Komai-Koma, M., Gilchrist, D. S., McKenzie, A. N., Goodyear, C. S., Xu, D., and Liew, F. Y. (2011) IL-33 acti-vates B1 cells and exacerbates contact sensitivity, J. Immunol., 186, 2584–2591.
Kusano, S., Kukimoto-Niino, M., Hino, N., Ohsawa, N., Ikutani, M., Takaki, S., Sakamoto, K., Hara-Yokoyama, M., Shirouzu, M., Takatsu, K., and Yokoyama, S. (2012) Structural basis of interleukin-5 dimer recognition by its α receptor, Protein Sci., 21, 850–864.
Oshikawa, K., Yanagisawa, K., Tominaga, S. I., and Sugiyama, Y. (2002) ST2 protein induced by inflammatory stimuli can modulate acute lung inflammation, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 299, 18–24.
Kurowska-Stolarska, M., Stolarski, B., Kewin, P., Murphy, G., Corrigan, C. J., Ying, S., Pitman, N., Mirchandani, A., Rana, B., van Rooijen, N., Shepherd, M., McSharry, C., McInnes, I. B., Xu, D., and Liew, F. Y. (2009) IL-33 ampli-fies the polarization of alternatively activated macrophages that contribute to airway inflammation, J. Immunol., 183, 6469–6477.
Espinassous, Q., Garcia-de-Paco, E., Garcia-Verdugo, I., Synguelakis, M., von Aulock, S., Sallenave, J. M., McKenzie, A. N., and Kanellopoulos, J. (2009) IL-33 enhances lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory cytokine produc-tion from mouse macrophages by regulating lipopolysaccha-ride receptor complex, J. Immunol., 183, 1446–1455.
Neill, D. R., Wong, S. H., Bellosi, A., Flynn, R. J., Daly, M., Langford, T. K., Bucks, C., Kane, C. M., Fallon, P. G., Pannell, R., Jolin, H. E., and McKenzie, A. N. (2010) Nuocytes represent a new innate effector leukocyte that mediates type-2 immunity, Nature, 464, 1367–1370.
Chang, Y. J., Kim, H. Y., Albacker, L. A., Baumgarth, N., McKenzie, A. N., Smith, D. E., Dekruyff, R. H., and Umetsu, D. T. (2011) Innate lymphoid cells mediate influenza-induced airway hyper-reactivity independently of adaptive immunity, Nat. Immunol., 12, 631–638.
Klein Wolterink, R. G., Kleinjan, A., van Nimwegen, M., Bergen, I., De Bruijn, M., Levani, Y., and Hendriks, R. W. (2012) Pulmonary innate lymphoid cells are major produc-ers of IL-5 and IL-13 in murine models of allergic asthma, Eur. J. Immunol., 42, 1106–1116.
Kim, H. Y., Chang, Y. J., Subramanian, S., Lee, H. H., Albacker, L. A., Matangkasombut, P., Savage, P. B., McKenzie, A. N., Smith, D. E., Rottman, J. B., DeKruyff, R. H., and Umetsu, D. T. (2012) Innate lymphoid cells responding to IL-33 mediate airway hyperreactivity inde-pendently of adaptive immunity, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 129, 216–227.
Barlow, J. L., Bellosi, A., Hardman, C. S., Drynan, L. F., Wong, S. H., Cruickshank, J. P., and McKenzie, A. N. (2012) Innate IL-13-producing nuocytes arise during aller-gic lung inflammation and contribute to airways hyperreac-tivity, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 129, 191–198.
Ohno, T., Morita, H., Arae, K., Matsumoto, K., and Nakae, S. (2012) Interleukin-33 in allergy, Allergy, 67, 1203–1214.
Liu, X., Li, M., Wu, Y., Zhou, Y., Zeng, L., and Huang, T. (2009) Anti-IL-33 antibody treatment inhibits airway inflammation in a murine model of allergic asthma, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 386, 181–185.
Holgate, S. T. (2011) The sentinel role of the airway epithe-lium in asthma pathogenesis, Immunol. Rev., 242, 205–219.
Virchow, J. C. (2012) Emergency checklist: asthma attack, MMW Fortschr. Med., 154, 55–56.
Kearley, J., Buckland, K. F., Mathie, S. A., and Lloyd, C. M. (2009) Resolution of allergic inflammation and airway hyperreactivity is dependent upon disruption of the T1/ST2-IL-33 pathway, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med., 179, 772–781.
Jarvis, D., Newson, R., Lotvall, J., Hastan, D., Tomassen, P., Keil, T., Gjomarkaj, M., Forsberg, B., Gunnbjornsdottir, M., Minov, J., Brozek, G., Dahlen, S. E., Toskala, E., Kowalski, M. L., Olze, H., Howarth, P., Kramer, U., Baelum, J., Loureiro, C., Kasper, L., Bousquet, P. J., Bousquet, J., Bachert, C., Fokkens, W., and Burney, P. (2012) Asthma in adults and its association with chronic rhinosinusitis: the GA2LEN survey in Europe, Allergy, 67, 91–98.
Lozano, R., Naghavi, M., Foreman, K., Lim, S., Shibuya, K., Aboyans, V., Abraham, J., Adair, T., Aggarwal, R., Ahn, S. Y., Alvarado, M., Anderson, H. R., Anderson, L. M., Andrews, K. G., Atkinson, C., Baddour, L. M., Barker-Collo, S., Bartels, D. H., Bell, M. L., Benjamin, E. J., Bennett, D., Bhalla, K., Bikbov, B., Bin Abdulhak, A., Birbeck, G., Blyth, F., Bolliger, I., Boufous, S., Bucello, C., Burch, M., Burney, P., Carapetis, J., Chen, H., Chou, D., Chugh, S. S., Coffeng, L. E., Colan, S. D., Colquhoun, S., Colson, K. E., Condon, J., Connor, M. D., Cooper, L. T., Corriere, M., Cortinovis, M., De Vaccaro, K. C., Couser, W., Cowie, B. C., Criqui, M. H., Cross, M., Dabhadkar, K. C., Dahodwala, N., De Leo, D., Degenhardt, L., Delossantos, A., Denenberg, J., Des Jarlais, D. C., Dharmaratne, S. D., Dorsey, E. R., Driscoll, T., Duber, H., Ebel, B., Erwin, P. J., Espindola, P., Ezzati, M., Feigin, V., Flaxman, A. D., Forouzanfar, M. H., Fowkes, F. G., Franklin, R., Fransen, M., Freeman, M. K., Gabriel, S. E., Gakidou, E., Gaspari, F., Gillum, R. F., Gonzalez-Medina, D., Halasa, Y. A., Haring, D., Harrison, J. E., Havmoeller, R., Hay, R. J., Hoen, B., Hotez, P. J., Hoy, D., Jacobsen, K. H., James, S. L., Jasrasaria, R., Jayaraman, S., Johns, N., Karthikeyan, G., Kassebaum, N., Keren, A., Khoo, J. P., Knowlton, L. M., Kobusingye, O., Koranteng, A., Krishnamurthi, R., Lipnick, M., Lipshultz, S. E., Ohno, S. L., Mabweijano, J., MacIntyre, M. F., Mallinger, L., March, L., Marks, G. B., Marks, R., Matsumori, A., Matzopoulos, R., Mayosi, B. M., McAnulty, J. H., McDermott, M. M., McGrath, J., Mensah, G. A., Merriman, T. R., Michaud, C., Miller, M., Miller, T. R., Mock, C., Mocumbi, A. O., Mokdad, A. A., Moran, A., Mulholland, K., Nair, M. N., Naldi, L., Narayan, K. M., Nasseri, K., Norman, P., O’Donnell, M., Omer, S. B., Ortblad, K., Osborne, R., Ozgediz, D., Pahari, B., Pandian, J. D., Rivero, A. P., Padilla, R. P., Perez-Ruiz, F., Perico, N., Phillips, D., Pierce, K., Pope, C. A., 3rd, Porrini, E., Pourmalek, F., Raju, M., Ranganathan, D., Rehm, J. T., Rein, D. B., Remuzzi, G., Rivara, F. P., Roberts, T., De Leon, F. R., Rosenfeld, L. C., Rushton, L., Sacco, R. L., Salomon, J. A., Sampson, U., Sanman, E., Schwebel, D. C., Segui-Gomez, M., Shepard, D. S., Singh, D., Singleton, J., Sliwa, K., Smith, E., Steer, A., Taylor, J. A., Thomas, B., Tleyjeh, I. M., Towbin, J. A., Truelsen, T., Undurraga, E. A., Venketasubramanian, N., Vijayakumar, L., Vos, T., Wagner, G. R., Wang, M., Wang, W., Watt, K., Weinstock, M. A., Weintraub, R., Wilkinson, J. D., Woolf, A. D., Wulf, S., Yeh, P. H., Yip, P., Zabetian, A., Zheng, Z. J., Lopez, A. D., Murray, C. J., AlMazroa, M. A., and Memish, Z. A. (2012) Global and regional mor-tality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010, Lancet, 380, 2095–2128.
Akdis, C. A., and Akdis, M. (2015) Mechanisms of aller-gen-specific immunotherapy and immune tolerance to allergens, World Allergy Organ. J., 8, 17.
Boyman, O., Kaegi, C., Akdis, M., Bavbek, S., Bossios, A., Chatzipetrou, A., Eiwegger, T., Firinu, D., Harr, T., Knol, E., Matucci, A., Palomares, O., Schmidt-Weber, C., Simon, H. U., Steiner, U. C., Vultaggio, A., Akdis, C. A., and Spertini, F. (2015) EAACI IG biologicals task force paper on the use of biologic agents in allergic disorders, Allergy, 70, 727–754.
Shilovskiy, I. P., Babakhin, A. A., Shershakova, N. N., Kamyshnikov, O. Y., Sundukova, M. S., Gaisina, A. R., Laskin, A. A., Buzuk, A. M., Ivanova, A. S., and Khaitov, M. R. (2015) Adjuvant and adjuvant-free protocols produce similar phenotypes of allergic asthma in mice, Curr. Trends Immunol., 16, 79–91.
Tashiro, H., Takahashi, K., Hayashi, S., Kato, G., and Kurata, K. (2016) Interleukin-33 from monocytes recruit-ed to the lung contributes to house dust mite-induced air-way inflammation in a mouse model, PLoS One, 11, 1–16.
Yagami, A., Orihara, K., Morita, H., Futamura, K., Hashimoto, N., Matsumoto, K., Saito, H., and Matsuda, A. (2010) IL-33 mediates inflammatory responses in human lung tissue cells, J. Immunol., 185, 5743–5750.
Bunting, M. M., Shadie, A. M., Flesher, R. P., Nikiforova, V., Garthwaite, L., Tedla, N., Herbert, C., and Kumar, R. K. (2013) Interleukin-33 drives activation of alveolar macrophages and airway inflammation in a mouse model of acute exacerbation of chronic asthma, Biomed. Res. Int., 2013, 250938.
Kondo, Y., Yoshimoto, T., Yasuda, K., Futatsugi-Yumikura, S., Morimoto, M., Hayashi, N., Hoshino, T., Fujimoto, J., and Nakanishi, K. (2008) Administration of IL-33 induces airway hyperresponsiveness and goblet cell hyperplasia in the lungs in the absence of adaptive immune system, Int. Immunol., 20, 791–800.
Stolarski, B., Kurowska-Stolarska, M., Kewin, P., Xu, D., and Liew, F. Y. (2010) IL-33 exacerbates eosinophil-medi-ated airway inflammation, J. Immunol., 185, 3472–3480.
Sjoberg, L. C., Nilsson, A. Z., Lei, Y., Gregory, J. A., Adner, M., and Nilsson, G. P. (2017) Interleukin 33 exac-erbates antigen driven airway hyperresponsiveness, inflam-mation and remodeling in a mouse model of asthma, Sci. Rep., 7, 1–10.
Zhiguang, X., Wei, C., Steven, R., Wei, D., Wei, Z., Rong, M., Zhanguo, L., and Lianfeng, Z. (2010) Over-expression of IL-33 leads to spontaneous pulmonary inflammation in mIL-33 transgenic mice, Immunol. Lett., 131, 159–165.
Han, H., and Zie, S. F. (2017) Intradermal administration of IL-33 induces allergic airway inflammation, Sci. Rep., 7, 1–8.
Coyle, A. J., Lloyd, C., Tian, J., Nguyen, T., Erikkson, C., Wang, L., Ottoson, P., Persson, P., Delaney, T., Lehar, S., Lin, S., Poisson, L., Meisel, C., Kamradt, T., Bjerke, T., Levinson, D., and Gutierrez-Ramos, J. C. (1999) Crucial role of the interleukin 1 receptor family member T1/ST2 in T helper cell type 2-mediated lung mucosal immune responses, J. Exp. Med., 190, 895–902.
Shadie, A. M., Herbert, C., and Kumar, R. K. (2014) Ambient particulate matter induces an exacerbation of air-way inflammation in experimental asthma: role of inter-leukin-33, Clin. Exp. Immunol., 177, 491–499.
Lei, Y., Boinapally, V., Zoltowska, A., Adner, M., and Hellman, L. (2015) Vaccination against IL-33 inhibits air-way hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in a house dust mite model of asthma, PLoS One, 10, 1–15.
Mangan, N. E., Dasvarma, A., McKenzie, A. N., and Fallon, P. G. (2007) T1/ST2 expression on Th2 cells nega-tively regulates allergic pulmonary inflammation, Eur. J. Immunol., 37, 1302–1312.
Zoltowska, A. M., Lei, Y., Fuchs, B., Rask, C., Adner, M., and Nilsson, G. P. (2016) The interleukin-33 receptor ST2 is important for the development of peripheral airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in a house dust mite mouse model of asthma, Clin. Exp. Allergy, 46, 479–490.
Oboki, K., Ohno, T., Kajiwara, N., Arae, K., Morita, H., Ishii, A., Nambu, A., Abe, T., Kiyonari, H., Matsumoto, K., Sudo, K., Okumura, K., Saito, H., and Nakae, S. (2010) IL-33 is a crucial amplifier of innate rather than acquired immunity, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 107, 18581–18586.
Louten, J., Rankin, A. L., Li, Y., Murphy, E. E., Beaumont, M., Moon, C., Bourne, P., McClanahan, T. K., Pflanz, S., and De Waal Malefyt, R. (2011) Endogenous IL-33 enhances Th2 cytokine production and T-cell responses during allergic airway inflammation, Int. Immunol., 23, 307–315.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M. R. Khaitov, A. R. Gaisina, I. P. Shilovskiy, V. V. Smirnov, G. V. Ramenskaia, A. A. Nikonova, R. M. Khaitov, 2018, published in Biokhimiya, 2018, Vol. 83, No. 1, pp. 19-33.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khaitov, M.R., Gaisina, A.R., Shilovskiy, I.P. et al. The role of interleukin-33 in pathogenesis of bronchial asthma. New experimental data. Biochemistry Moscow 83, 13–25 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297918010029
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297918010029