Abstract
Background
Although many experiences using the da Vinci Robot System have been reported by several groups, there is substantial controversy over the role of the robot in thyroidectomy. We performed a systematic review and meta-analyses in order to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of robotic thyroidectomy (RT) compared with open thyroidectomy (OT) in thyroid cancer.
Methods
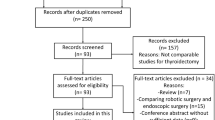
A literature search for the systematic review was conducted using English databases (Ovid MEDLINE, Ovid EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library), as well as domestic databases, up to June 2014.Outcomes of interest included demographic characteristics, adverse events and complications, and outcomes of effectiveness.
Results
Fourteen publications including 3,136 cases were finally selected for the systematic review and meta-analysis. RT was associated with an equivalent complication rate including transient and permanent hypocalcemia, transient and permanent recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy, bleeding, chyle leakage, seroma, length of hospital stay, and postoperative thyroglobulin level when compared with OT. RT also had lesser blood loss (weighted mean difference [WMD]−0.28, p = 0.04), better cosmetic satisfaction (odds ratio 4.79, p < 0.001), and lower level of swallowing impairment (WMD −4.17, p < 0.001) than OT. OT was in favor of operation time (WMD 39.77, p < 0.001) and retrieved lymph nodes (WMD −0.62, p = 0.02) compared with RT.
Conclusions
RT seems to be associated with a lesser amount of estimated blood loss, better cosmetic satisfaction, and a low level of swallowing impairment, while OT was associated with a shorter operation time and more retrieved lymph nodes. Randomized clinical trials with large samples and comparative studies that reflect long-term follow-up data are needed to validate our findings.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giddings AE. The history of thyroidectomy. J R Soc Med. 1998;91 Suppl 33:3-6.
Welbourn RB. Highlights from endocrine surgical history. World J Surg. 1996;20(5):603-612.
Ohgami M, Ishii S, Arisawa Y, et al. Scarless endoscopic thyroidectomy: breast approach for better cosmesis. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2000;10(1):1-4.
Duncan TD, Rashid Q, Speights F, Ejeh I. Transaxillary endoscopic thyroidectomy: an alternative to traditional open thyroidectomy. J Natl Med Assoc. 2009;101(8):783-787.
Pellegriti G, Frasca F, Regalbuto C, Squatrito S, Vigneri R. Worldwide increasing incidence of thyroid cancer: update on epidemiology and risk factors. J Cancer Epidemiol. 2013;2013:965212.
Terris DJ. Surgical approaches to the thyroid gland: which is the best for you and your patient? JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013;139(5):515-517.
Tan CT, Cheah WK, Delbridge L. “Scarless” (in the neck) endoscopic thyroidectomy (SET): an evidence-based review of published techniques. World J Surg. 2008;32(7):1349-1357.
Yeung GH. Endoscopic thyroid surgery today: a diversity of surgical strategies. Thyroid. 2002;12(8):703-706.
Kandil EH, Noureldine SI, Yao L, Slakey DP. Robotic transaxillary thyroidectomy: an examination of the first one hundred cases. J Am Coll Surg. 2012;214(4):558-564; discussion 564-556.
Muenscher A, Dalchow C, Kutta H, Knecht R. The endoscopic approach to the neck: a review of the literature, and overview of the various techniques. Surg Endosc. 2011;25(5):1358-1363.
Kang SW, Jeong JJ, Yun JS, et al. Robot-assisted endoscopic surgery for thyroid cancer: experience with the first 100 patients. Surg Endosc. 2009;23(11):2399-2406.
Lee J, Nah KY, Kim RM, Ahn YH, Soh EY, Chung WY. Differences in postoperative outcomes, function, and cosmesis: open versus robotic thyroidectomy. Surg Endosc. 2010;24(12):3186-3194.
Kuppersmith RB, Holsinger FC. Robotic thyroid surgery: an initial experience with North American patients. Laryngoscope. 2011;121(3):521-526.
Ishikawa N, Kawaguchi M, Moriyama H, Tanaka N, Watanabe G. First robot-assisted thyroidectomy in Japan performed using a standard da Vinci surgical system. Artif Organs. 2012;36(5):496-498.
Sun GH, Peress L, Pynnonen MA. Systematic review and meta-analysis of robotic vs conventional thyroidectomy approaches for thyroid disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014;150(4):520-532.
Lang BH, Wong CK, Tsang JS, Wong KP, Wan KY. A systematic review and meta-analysis comparing surgically-related complications between robotic-assisted thyroidectomy and conventional open thyroidectomy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21(3):850-861.
Jackson NR, Yao L, Tufano RP, Kandil EH. Safety of robotic thyroidectomy approaches: meta-analysis and systematic review. Head Neck. 2014;36(1):137-143.
Slim K, Nini E, Forestier D, Kwiatkowski F, Panis Y, Chipponi J. Methodological Index for Non-Randomized Studies (MINORS): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J Surg. 2003;73(9):712-716.
Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2005;5:13.
Kang SW, Lee SH, Park JH, et al. A comparative study of the surgical outcomes of robotic and conventional open modified radical neck dissection for papillary thyroid carcinoma with lateral neck node metastasis. Surg Endosc. 2012;26(11):3251-3257.
Lee J, Kwon IS, Bae EH, Chung WY. Comparative analysis of oncological outcomes and quality of life after robotic versus conventional open thyroidectomy with modified radical neck dissection in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma and lateral neck node metastases. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(7):2701-2708.
Ryu HR, Lee J, Park JH, et al. A comparison of postoperative pain after conventional open thyroidectomy and transaxillary single-incision robotic thyroidectomy: a prospective study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(7):2279-2284.
Aliyev S, Taskin HE, Agcaoglu O, et al. Robotic transaxillary total thyroidectomy through a single axillary incision. Surgery. 2013;153(5):705-710.
Noureldine SI, Jackson NR, Tufano RP, Kandil E. A comparative North American experience of robotic thyroidectomy in a thyroid cancer population. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2013;398(8):1069-1074.
Kim WW, Kim JS, Hur SM, et al. Is robotic surgery superior to endoscopic and open surgeries in thyroid cancer? World J Surg. 2011;35(4):779-784.
Cho BC, Jung HB, Cho ST, et al. Our experiences with robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy: orthotopic neobladder by the suprapubic incision method. Korean J Urol. 2012;53(11):766-773.
Tae K, Song CM, Ji YB, Kim KR, Kim JY, Choi YY. Comparison of surgical completeness between robotic total thyroidectomy versus open thyroidectomy. Laryngoscope. 2014;124(4):1042-1047.
Yi O, Yoon JH, Lee YM, et al. Technical and oncologic safety of robotic thyroid surgery. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(6):1927-1933.
Kim JA, Kim JS, Chang MS, Yoo YK, Kim DK. Influence of carbon dioxide insufflation of the neck on intraocular pressure during robot-assisted endoscopic thyroidectomy: a comparison with open thyroidectomy. Surg Endosc. 2013;27(5):1587-1593.
Lee KE, Koo do H, Im HJ, et al. Surgical completeness of bilateral axillo-breast approach robotic thyroidectomy: comparison with conventional open thyroidectomy after propensity score matching. Surgery. 2011;150(6):1266-1274.
Yoo JY, Chae YJ, Cho HB, Park KH, Kim JS, Lee SY. Comparison of the incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting between women undergoing open or robot-assisted thyroidectomy. Surg Endosc. 2013;27(4):1321-1325.
Tae K, Kim KY, Yun BR, et al. Functional voice and swallowing outcomes after robotic thyroidectomy by a gasless unilateral axillo-breast approach: comparison with open thyroidectomy. Surg Endosc. 2012;26(7):1871-1877.
Tae K, Ji YB, Jeong JH, Lee SH, Jeong MA, Park CW. Robotic thyroidectomy by a gasless unilateral axillo-breast or axillary approach: our early experiences. Surg Endosc. 2011;25(1):221-228.
Reeves BC Deeks J, Higgins JPT, Wells GA. Including non-randomized studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.1. The Cochrane Collaboration; 2008.
Lee S, Ryu HR, Park JH, et al. Early surgical outcomes comparison between robotic and conventional open thyroid surgery for papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Surgery. 2012;151(5):724-730.
Kim BS, Kang KH, Kang H, Park SJ. Central neck dissection using a bilateral axillo-breast approach for robotic thyroidectomy: comparison with conventional open procedure after propensity score matching. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2014;24(1):67-72.
Acknowledgment
This study was funded by the National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency in Korea (NC13-007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Son, S.K., Kim, J.H., Bae, J.S. et al. Surgical Safety and Oncologic Effectiveness in Robotic versus Conventional Open Thyroidectomy in Thyroid Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann Surg Oncol 22, 3022–3032 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4375-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4375-9