Abstract
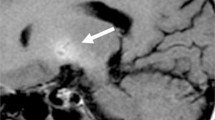
Neurological disorders similar to parkinsonian syndrome and signal hyperintensity in brain on T1-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) images have been reported in patients receiving long-term total parenteral nutrition (TPN). These symptoms have been associated with manganese (Mn) depositions in brain. Although alterations of signal intensity on T1-weighted MR images in brain and of Mn concentration in blood are theoretically considered good indices for estimating Mn deposition in brain, precise correlations between these parameters have not been demonstrated as yet.
Male Sprague-Dawley rats received TPN with 10-fold the clinical dose of the trace element preparation (TE-5) for 7 d. At 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 wk post-TPN, the cortex, striatum, midbrain, and cerebellum were evaluated by MR images, and Mn concentration in blood and Mn content in these brain sites were measured by atomic absorption spectrometry. Immediately after TPN termination, signal hyperintensity in brain sites and elevated Mn content in blood and brain sites were observed. These values recovered at 4 wk post-TPN. A positive correlation was observed between either the signal intensity in certain brain sites or Mn content in blood and the relevant brain sites.
Our observations suggest that the Mn concentration in blood and signal intensity in the brain sites on T1-weighted MR images are reliable indices for monitoring Mn contents in brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. J. Dudrick, D. W. Wilmore, H. M. Vars, and J. E. Rhoads, Long-term total parenteral nutrition with growth, development, and positive nitrogen balance, Surgery 64, 134–142 (1968).
P. Guthrie and W. W. Turner, Peripheral and central nutritional support, Journal of National Intravenous Therapy Association 9, 393–398 (1986).
M. G. Shills, Guidelines for essential trace element preparations for parenteral use, Am. J. Hosp. Pharm. 241, 2051–2054 (1974).
H. L. Green, M. Hambidge, and Y. F. Herman, Trace elements and vitamins in parenteral nutrition in infancy and children, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 46, 131–45 (1974).
A. Ejima, T. Imamura, S. Nakamura, H. Sato, K. Matsumoto, and S. Momono, Manganese intoxication during total parenteral nutrition, Lancet 339, 426 (1992).
S. A. Mirowitz, T. J. Wetrich, and J. D. Hirsch, Hyperintense basal ganglia on T1-weighted MR images in patients receiving parenteral nutrition, Radiology 181, 117–120 (1991).
J. M. E. Fell, A. P. Reynolds, N. Meadows, K. Khan, S. G. Long, G. Quaghebeur, et al., Manganese toxicity in children. receiving long term parenteral nutrition, Lancet 347, 1218–1221 (1991).
G. Alves, J. Thiebof, A. Tracqui, T. Delangre, C. Guedon, and E. Lerebours, Neurological disorders due to brain manganese deposition in jaundiced patients receiving long-term parenteral nutrition, JPEN 21, 41–45 (1997).
J. Ono, K. Harada, R. Kodama, K. Sakurai, H. Tajiri, Y. Takagi, et al., Manganese deposition in the brain during long-term total parenteral nutrition, JPEN 19, 310–312 (1995).
I. Mena, O. Marin, S. Fuenzolta, and G. C. Cotzias, Chronic manganese poisoning: clinical picture and manganese turnover, Neurology 17, 128–136 (1967).
R. E. London, G. Toney, S. A. Gabel, and A. Funk, Magnetic resonance imaging studies of the brains of anesthetized rats treated with manganese chloride, Brain Res. Bull. 23, 229–235 (1989).
A. Takeda, T. Akiyama, J. Sawashita, and S. Okada, Brain uptake of trace metals, zinc and manganese in rats, Brain Res. 640, 341–344 (1994).
H. Eriksson, K. Miste, L. O. Plantin, F. Fonnum, K. G. Hedstrom, E. Theodorsson-Norheim, et al., Effects of manganese oxide on monkeys as revealed by combined neurochemical, histological and neurophysiological evaluation, Arch. Toxicol. 61, 46–52 (1987).
H. Shinotoh, B. J. Snow, K. A. Hewitt, K. A. Hewitt, B. D. Pate, D. Doudet, et al., MRI and PET studies of manganese-intoxicated monkeys, Neurology 45, 1199–1204 (1995).
H. Eriksson, J. Tedroff, K. A. Thuomas, S. M. Aquilonius, P. Hartvig, K. J. Fasth, et al., Manganese induced brain lesions in Macaca fasciculoris as revealed by positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance, Arch. Toxicol. 66, 403–407 (1992).
C. C. Huang, N. S. Chu, C. S. Lu, and J. D. Wang, Chronic manganese intoxication, Arch. Neurol. 46, 1104–1106 (1989).
M. C. Newland, T. L. Ceckler, J. H. Kordower, and B. Weiss, Visualizing manganese in the primate basal ganglia with magnetic resonance imaging, Exp. Neurol. 106, 251–258 (1989).
H. Chaki, A. Matsuda, K. Yamamoto, Y. Kokuba, M. Kataoka, M. Sato, et al., Significance of magnetic resonance image and blood managanese measurement fo the assessment of brain manganese during total parenteral nutrition in rats, Biol. Trace Element Res. 63, 37–50 (1998).
E. Steiger, H. M. Vars, and S. J. Dudrick, A technique for long term intravenous feeding in unrestrained rats, Arch. Surg. 104, 330–332 (1992).
A. Matsuda, M. Kimura, T. Takeda, M. Kataoka, M. Sato, and Y. Itokawa, Changes in manganese content of mononuclear blood cells in patients receiving total parenteral nutrition, Clin. Chem. 40, 829–832 (1994).
A. Matsuda, M. Kimura, M. Kataoka, S. Ohkuma, M. Sato, and Y. Itokawa, Quantifying managanese in lymphocytes to assess manganese nutritional status, Clin. Chem. 35, 1939–1941 (1989).
D. A. Hankins, M. C. Riella, B. H. Scribner, and A. L. Babb, Whole blood trace element concentrations during total parenteral nutrition, Surgery 79, 674–677 (1976).
A. Matsuda, S. Kumadani, M. Kataoka, M. Sato, M. Kimura, and Y. Itokawa, Influence of repeated intravenous administration of manganese on electroencephalogram, behavior and brain manganese concentration in rats, Biomed Res. Trace Elements 3, 29–39 (1992).
D. Krieger, S. Krieger, O. Jansen, P. Gass, L. Theilmann, and H. Lichtnecker, Manganese and chronic hepatic encephalopathy, Lancet 346, 270–273 (1995).
H. Sakurai, M. Nishida, T. Yoshimura, J. Takada, and M. Koyama, Partition of divalent and total manganese in organs and subcellular organelles of MnCl2 treated rats studied by ESR and nutim activity analysis, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 841, 208–214 (1985).
E. P. Browllet, L. Shinobu, U. McGarvey, F. Hochberg, and M. F. Beal, Manganese injection into rat striatum produces excitoxic lesion by impairing energy metabolism, Exp. Neurol. 120, 89–94 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaki, H., Furuta, S., Matsuda, A. et al. Magnetic resonance image and blood manganese concentration as indices for manganese content in the brain of rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 74, 245–257 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:74:3:245
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:74:3:245