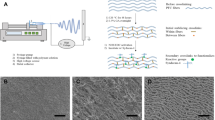
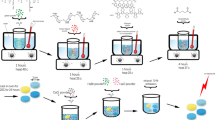
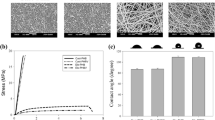
Abstract
It has been recognized that seeding vascular bypass grafts with endothelial cells is the ideal method of improving their long-term patency rates. The aim of this study was to assess the in vitro cytocompatibility of a novel silica nanocomposite, polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane-poly(carbonate-urea)urethane (POSS-PCU) and hence elicit its feasibility at the vascular interface for potential use in cardiovascular devices such as vascular grafts. Using primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC), cell viability and adhesion were studied using AlamarBlue assays, whereas cell proliferation on the polymer was assessed using the PicoGreen dye assay. Cellular confluence and morphology on the nanocomposite were analyzed using light and electron microscopy, respectively. Our results showed that there was no significant difference between cell viability in standard culture media and POSS-PCU. Endothelial cells were capable of adhering to the polymer within 30 min of contact (Student's t-test, p<0.05) with no difference between POSS-PCU and control cell culture plates. POSS-PCU was also capable of sustaining good cell proliferation for up to 14d even from low seeding densities (1.0×103 cells/cm2) and reaching saturation by 21 d. Microscopic analysis showed evidence of optimal endothelial cell adsorption morphology with the absence of impaired motility and morphogenesis. In conclusion, these results support the application of POSS-PCU as a suitable biomaterial scaffold in bio-hybrid vascular prostheses and biomedical devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kidane, A. G., Salacinski, H., Tiwari, A., Bruckdorfer, K. R., and Seifalian, A. M. (2004) Anticoagulant and antiplatelet agents: their clinical and device application(s) together with usages to engineer surfaces. Biomacromolecules 5, 798–813.
Baguneid, M., Murray, D., Salacinski, H. J., et al. (2004) Shear-stress preconditioning and tissue-engineering-based paradigms for generating arterial substitutes. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 39, 151–157.
Kannan, R. Y., Salacinski, H. J., Sales, K., Butler, P., and Seifalian, A. M. (2005) The roles of tissue engineering and vascularisation in the development of micro-vascular networks: a review. Biomaterials 26, 1857–1875.
Salacinski, H. J., Goldner, S., Giudiceandrea, A., et al. (2001) The mechanical behavior of vascular grafts: a review. J. Biomater. Appl. 15, 241–278.
Tai, N. R., Salacinski, H. J., Edwards, A., Hamilton, G., and Seifalian, A. M. (2000) Compliance properties of conduits used in vascular reconstruction. Br. J. Surg. 87, 1516–1524.
Brossollet, L. J. (1992) Mechanical issues in vascular grafting: review. Int. J. Artif. Organs 15, 579–584.
Lau, H. and Cheng, S. W. (2001) Is the preferential use of ePTFE grafts in femorofemoral bypass justified? Ann. Vasc. Surg. 15, 383–387.
Tiwari, A., DiSalvo, C., Walesby, R., Hamilton, G., and Seifalian, A. M. (2003) Mediastinal fat: a source of cells for tissue engineering of coronary artery bypass grafts. Microvasc. Res. 65, 61–64.
Tiwari, A., Kidane, A., Salacinski, H. J., Punshon, G., Hamilton, G., and Seifalian, A. M. (2003) Improving endothelial cell retention for single stage seeding of prosthetic grafts: use of polymer sequences of arginine-glycine-aspartate (RGD). Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 25, 325–329.
Deutsch, M., Meinhart, J., Fischlein, T., Preiss, P., and Zilla, P. (1999) Clinical autologous in vitro endothelialization of infrainguinal ePTFE grafts in 100 patients: a 9-year experience. Surgery 126, 847–855.
Meinhart, J. G., Deutsch, M., Fischlein, T., Howanietz, N., Froschl, A., and Zilla, P. (2001) Clinical autologous in vitro endothelialization of 153 infrainguinal ePTFE grafts. Ann. Thorac Surg. 71, S327-S331.
Seifalian, A. M., Tiwari, A., Hamilton, G., and Salacinski, H. J. (2002) Improving the clinical patency of prosthetic vascular and coronary bypass grafts: the role of seeding and tissue engineering. Artif. Organs 26, 307–320.
Zilla, P., Fasol, R., Deutsch, M. et al. (1987) Endothelial cell seeding of polytetrafluoroethylene vascular grafts in humans: a preliminary report. J. Vasc. Surg. 6, 535–541.
Tiwari, A., Cheng, K., Salacinski, H. J., Hamilton, G., and Seifalian, A. M. (2003) Improving compliance at peripheral arterial and cardiovascular anastomosis: the effect of suture materials and techniques. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 25, 325–329.
Tai, N. R., Salacinski, H. J., Edwards, A., Hamilton, G., and Seifalian, A. M. (2000) Compliance properties of conduits used in vascular reconstruction. Br. J. Surg. 87, 1516–1524.
Berrocal, M. J., Badr, I. H., Gao, d., and Bachas, L. G. (2001) Reducing the thrombogenicity of ion-selective electrode membranes through the use of a silicone-modified segmented polyurethane. Anal. Chem. 73, 5328–5333.
Park, J. H. and Bae, Y. H. (2002) Hydrogels based on poly(ethylene oxide) and poly(tetramethylene oxide) or poly(dimethyl siloxane): synthesis, characterization, in vitro protein adsorption and platelet adhesion. Biomaterials 23, 1797–1808.
Nyilas, E. and Ward, R. S., Jr. (1977) Development of blood-compatible elastomers. V. Surface structure and blood compatibility of avcothane elastomers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 11, 69–84.
Hoffman, D., Gong, G., Pinchuk, L., and Sisto, D. (1993) Safety and intracardiac function of a silicone-polyurethane elastomer designed for vascular use. Clin. Mater. 13, 95–100.
Schubert, M. A., Wiggins, M. J., Anderson, J. M., and Hiltner, A. (1997) Role of oxygen in biodegradation of poly(etherurethane urea) elastomers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 34, 519–530.
Kao, W. J. (1999) Evaluation of protein-modulated macrophage behavior on biomaterials: designing biomimetic materials for cellular engineering. Biomaterials 20, 2213–2221.
Salacinski, H. J., Hancock, S., and Seifalian, A. M. (2005) Polymer for use in conduits, medical devies and biomedical surface modification. Int. App. No. PCT/GB2005/000189.
Seifalian, A. M., Salacinski, H. J., Punshon, G., Krijgsman, B., and Hamilton, G. (2001) A new technique for measuring the cell growth and metabolism of endothelial cells seeded on vascular prostheses. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 55, 637–644.
Punshon, G., Vara, D. S., Sales, K. M., Kidane, A. G., Salacinski, H. J., and Seifalian, A. M. (2005) Interactions between endothelial cells and a poly(carbonate-silsesquioxane-bridge-urea)urethane. Biomaterials 26, 6271–6279.
International Standards Organization (ISO). (1992) Biological evaluation of medical devices: Tests for cytotoxicity: In vitro methods. Document No.: ISO 10993-5. ISO, Geneva, Switzerland, pp. 1–7.
Singer, V. L., Jones, L. J., Yue, S. T., and Haugland, R. P. (1997) Characterization of PicoGreen reagent and development of a fluorescence-based solution assay for double-stranded DNA quantitation. Anal. Biochem. 249, 228–238.
Park, J. C., Park, B. J., Lee, D. H., Suh, H., Kim, D. G., and Kwon, O. H. (2002) Evaluation of the cytotoxicity of polyetherurethane (PU) film containing zinc diethyldithiocarbamate (ZDEC) on various cell lines. Yonsei Med. J. 43, 518–526.
Cenni, E., Granchi, D., Verri, E., Remiddi, G., Cavedagna, D., and Di Leo, A. (2001) Evaluation of endothelial cell integrins afterin vitro contact with polyethylene terephthalate. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 12, 345–349.
Kidane, A. G., Salacinski, H. J., Punshon, G., Ramesh, B., Srai, K. S., and Seifalian, A. M. (2003) Synthesis and evaluation of amphiphilic RGD derivatives: uses for solvent casting in polymers and tissue engineering applications. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 41, 740–745.
Hamm, C. W., Schaachinger, V., Munzel, T., et al. (2003) Peptide-treated stent graft for the treatment of saphenous vein graft lesions: first clinical results. J. Invasive Cardiol. 15, 557–560.
Lehle, K., Buttstaedt, J., and Birnbaum, D. E. (2003) Expression of adhesion molecules and cytokines in vitro by endothelial cells seeded on various polymer surfaces coated with titaniumcarboxonitride. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 65A, 393–401.
Ai, H., Lvov, Y. M., Mills, D. K., Jennings, M., Alexander, J. S., and Jones, S. A. (2003) Coating and selective deposition of nanofilm on silicone rubber for cell adhesion and growth. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 38, 103–114.
Ai, H., Mills, D. K., Jonathan, A. S., and Jones, S. A. (2002) Celatin-glutaraldehyde cross-linking on silicone rubber to increase endothelial cell adhesion and growth. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 38, 487–492.
Lateef, S. S., Boateng, S., Hartman, T. J., Crot, C. A., Russell, B., and Hanley, L. (2002) GRGDSP peptide-bound silicone membranes withstand mechanical flexing in vitro and display enhanced fibroblast adhesion. Biomaterials 23, 3159–3168.
Salacinski, H. J., Tiwari, A., Hamilton, G., and Seifalian, A. M. (2001) Cellular engineering of vascular bypass grafts: role of chemical coatings for enhancing endothelial cell attachment. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 39, 609–618.
Wilsnack, R. E. (1976) Quantitative cell culture biocompatibility testing of medical devices and correlation to animal tests. Biomater. Med. Devices Artif. Organs 4, 235–261.
Hesse, Y., Kampmeier, J., Lang, G. K., Baldysiak-Figiel, A., and Lang, G. E. (2003) Adherence and viability of porcine lens epithelial cells on three different IOL materials in vitro. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 241, 823–826.
Lichtenhan, J. D. (1995) Polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes: building blocks for silsesquioxane-based polymers and hybrid materials. Comm. Inorg. Chem. 17, 115–130.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kannan, R.Y., Salacinski, H.J., Sales, K.M. et al. The endothelization of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nanocomposites. Cell Biochem Biophys 45, 129–136 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:45:2:129
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:45:2:129