Abstract
Objective
To assess if arachnoid cells have the capability to present antigen and activate T-lymphocytes after stimulation by bloody cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and to illuminate the mechanism of coagulation-initiated inflammation in the subarachnoid space after subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH).
Methods
Arachnoid cells were cultured, characterized, and examined by immunofluorescence for the basal expression of human leukocyte antigen-DR (HLA-DR). Expression of HLA-DR, after co-culturing arachnoid cells in vitro with bloody CSF, was investigated by immunofluorescence and flow cytometry (FCM). The variation of arachnoid cells’ ultrastructure was observed by transmission electron microscope (TEM). Arachnoid cells were co-cultured with peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). The content of soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2r) in culture medium was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Results
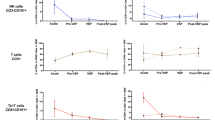
(1) Arachnoid cells were successfully cultured for many passages. The immunofluorescent staining was positive for HLA-DR in over 95% of the human arachnoid cells. The punctate HLA-DR was distributed in cytoplasm and not in the karyon. (2) After co-culturing arachnoid cells in vitro with bloody CSF, numerous particles with strong fluorescence appeared in the cytoplasm on Day 6. On Day 8, the quantity of particles and fluorescent intensity were maximal. FCM showed that the percentage of HLA-DR expressing cells was (2.5±0.4)% at the first 5 d, increasing to (60.8±3.6)% on Day 7. (3) After co-culturing arachnoid cells in vitro with bloody CSF, many lysosome and secondary lysosome particles were present in the cytoplasm. Hyperplasia of rough endoplasmic reticulum and enlarged cysts were observed, with numerous phagocytizing vesicles also observed at the edge of the arachnoid cells. (4) Arachnoid cells stimulated by bloody CSF were co-cultured in vitro with PBMCs. The content of sIL-2r in the culture medium, having been maintained at around 1.30 ng/ml during the first 3 d, had increased by Day 4. The content of sIL-2r peaked 7.53 ng/ml on Day 7 and then reduced gradually.
Conclusions
(1) Basic HLA-DR expression is present in arachnoid cells. (2) After stimulation by bloody CSF, arachnoid cells have the potential to serve as antigen presenting cells (APCs) and the ability to activate T-lymphocytes, indicating that arachnoid cells are involved in the mechanism of coagulation-initiated inflammation in the subarachnoid space after SAH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, Y.M., Gajdusek, C., London, S., Moon, C.T., Oh, C.W., Mayberg, M.R., 2002. Sustained arterial narrowing after prolonged exposure to perivascular endothelin. Neurosurgery, 50(4):843–849. [doi:10.1097/00006123-2002040 00-00029]
Akopov, S.E., Grigorian, M.R., Gabrielian, E.S., 1992. The endothelium-dependent relaxation of human middle cerebral arteries: effects of activated neutrophils. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 48(1):34–36. [doi:10.1007/BF01923601]
André, P., Prasad, K.S., Denis, C.V., He, M., Papalia, J.M., Hynes, R.O., Phillips, D.R., Wagner, D.D., 2002. CD40L stabilizes arterial thrombi by a β3 integrin-dependent mechanism. Nature Medicine, 8(3):247–252. [doi:10. 1038/nm0302-247]
Aydin, M.D., Akyol-Salman, I., Sahin, O., 2005. Histopathological changes in ciliary ganglion of rabbits with subarachnoid hemorrhage. International Journal of Neuroscience, 115(11):1595–1602. [doi:10.1080/002074 50590958079]
Bernstein, J.J., Karp, S.M., Goldberg, W.J., DeGiorgio, L.A., Blass, J.P., 1996. Human leptomeningeal-derived cells express GFAP and HLA-DR when grafted into rat spinal cord. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 14(5):681–687. [doi:10.1016/0736-5748(95)00096-8]
Chrapusta, S.J., Gorski, A., Mrowiec, T., Grieb, P., Andrychowski, J., Ryba, M.S., 1999. Tissue factor and factor VIIa receptor/ligand interactions induce proinflammatory effects in macrophages. Blood, 94(10):3413–3420.
Chrapusta, S.J., Gorski, A., Mrowiec, T., Grieb, P., Andrychowski, J., Ryba, M.S., 2000. Immune abnormalities in aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage patients: relation to delayed cerebral vasospasm. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology, 51(4):400–407. [doi:10.1046/j.1365-3083.2000.00694.x]
Claassen, J., Bernardini, G.L., Kreiter, K., Bates, J., Du, Y.E., Copeland, D., Sander Connolly, E., Mayer, S.A., 2001. Effect of cisternal and ventricular blood on risk delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage: the fisher scale revisited. Stroke, 32(9):2012–2016. [doi:10.1161/hs0901.095677]
Clatterbuck, R.E., Oshiro, E.M., Hoffman, P.A., Dietsch, G.N., Pardoll, D.M., Tamargo, R.J., 2002. Inhibition of vasospasm with lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 monoclonal antibody in a femoral artery model in rats. Journal of Neurosurgery, 97(3):676–682. [doi:10.3171/jns.2002.97.3.0676]
Eddleman, C.S., Hurley, M.C., Naidech, A.M., 2009. Endovascular options in the treatment of delayed ischemic neurological deficits due to cerebral vasospasm. Neurosurgical Focus, 26(3):6–8. [doi:10.3171/2008.11.FOCUS 08278]
Esmon, C.T., 2005. The interactions between inflammation and coagulation. British Journal of Haematology, 131(4): 417–430. [doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05753.x]
Frank, E., 1995. HLA-DR expression on arachnoid cells. A role in the fibrotic inflammation surrounding nerve roots in spondylotic cervical myelopathy. Spine, 20(19):2093–2096. [doi:10.1097/00007632-199510000-00004]
Frank, H., Boyce, W., 1983. Cytokeratin provides a specific marker for human arachnoid cells grown in vitro. Experimental Cell Research, 146(2):371–376. [doi:10.1016/0014-4827(83)90138-6]
Gomis, P., Tran-Dinh, Y.R., Sercombe, C., Sercombe, R., 2005. Dexamethasone preventing contractile and cytoskeletal protein changes in the rabbit basilar artery after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Journal of Neurosurgery, 102(4):715–720. [doi:10.3171/jns.2005.102.4.0715]
Harrod, C.G., Bendok, B.R., Batjer, H.H., 2005. Prediction of cerebral vasospasm in patients presenting with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a review. Neurosurgery, 56(4):633–654. [doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000156644.45384.92]
Hendryk, S., Jarzab, B., Josko, J., 2004. Increase of the IL-1 beta and IL-6 levels in CSF in patients with vasospasm following aneurysmal SAH. Neuroendocrinology Letters, 25(1/2):141–147.
Iuliano, B.A., Pluta, R.M., Jung, C., 2004. Endothelial dysfunction in a primate model of cerebral vasospasm. Journal of Neurosurgery, 100(2):287–295. [doi:10.3171/jns.2004.100.2.0287]
Jackowski, A., Crockard, A., Burnstock, G., Russell, R.R., Kristek, F., 1990. The time course of intracranial pathophysiological changes following experimental subarachnoid haemorrhage in the rat. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 10(6):835–849.
Jin, H., Gong, D., Adeegbe, D., Bayer, A.L., Rolle, C., Yu, A., Malek, T.R., 2006. Quantitative assessment concerning the contribution of IL-2Rβ for superantigen-mediated T cell responses in vivo. International Immunology, 18(4): 565–572. [doi:10.1093/intimm/dxh398]
Kim, K.Y., Kim, M.Y., Choi, H.S., 2002. Thrombin induces IL-10 production in microglia as a negative feedback regulator of TNF-α release. NeuroReport, 13(6):849–852. [doi:10.1097/00001756-200205070-00022]
Kubota, T., Handa, Y., Tsuchida, A., Kaneko, M., Kobayashi, H., Kubota, T., 1993. The kinetics of lymphocyte subsets and macrophages in subarachnoid space after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Stroke, 24(12):1993–2000.
Kwon, K.Y., Jeon, B.C., 2001. Cytokine levels in cerebrospinal fluid and delayed ischemic deficits (DCI) in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Journal of Korean Medical Science, 16(4):774–780 (in Korean).
Lan, W., Harmon, D.C., Wang, J.H., 2005. Activated endothelial interleukin-1, -6, and -8 concentrations and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression are attenuated by lidocaine. Anesthesia & Analgesia, 100(2):409–412. [doi: 10.1213/01.ANE.0000142113.39092.87]
Massicotte, E.M., Del Bigio, M.R., 1999. Human arachnoid villi response to subarachnoid hemorrhage: possible relationship to chronic hydrocephalus. Journal of Neurosurgery, 91(1):80–84. [doi:10.3171/jns.1999.91.1.0080]
Mathiesen, T., Lefvert, A.K., 1996. Cerebrospinal fluid and blood lymphocyte subpopulations following subarachnoid haemorrhage. British Journal of Neurosurgery, 10(1):89–92. [doi:10.1080/02688699650040584]
Mathiesen, T., Andersson, B., Loftenius, A., von Holst, H., 1993. Increased interleukin-6 levels in cerebrospinal fluid following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Journal of Neurosurgery, 78(4):562–567. [doi:10.3171/jns.1993.78.4.0562]
McMenamin, P.G., 1999. Distribution and phenotype of dendritic cells and resident tissue macrophages in the dura mater, leptomeninges, and choroid plexus of the rat brain as demonstrated in wholemount preparations. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 405(4):553–562. [doi:10. 1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19990322)405:4<553::AID-CNE8>3.3.CO;2-Y]
McMenamin, P.G., Wealthall, R.J., Deverall, M., Cooper, S.J., Griffin, B., 2003. Macrophages and dendritic cells in the rat meninges and choroid plexus: three-dimensional localisation by environmental scanning electron microscopy and confocal microscopy. Cell and Tissue Research, 313(3):259–269. [doi:10.1007/s00441-003-0779-0]
Motohashi, O., Suzuki, M., Shida, N., Umezawa, K., Ohtoh, T., Sakurai, Y., Yoshimoto, T., 1995a. Subarachnoid haemorrhage induced proliferation of leptomeningeal cells and deposition of extracellular matrices in the arachnoid granulations and subarachnoid space. Acta Neurochirurgica, 136(1/2):88–91. [doi:10.1007/BF01411441]
Motohashi, O., Suzuki, M., Yanai, N., Umezawa, K., Shida, N., Yoshimoto, T., 1995b. Thrombin and TGF-beta promote human leptomeningeal cell proliferation in vitro. Neuroscience Letters, 190(2):105–108. [doi:10.1016/0304-3940 (95)11513-V]
Murphy, M., Chen, J.N., George, D.L., 1991. Establishment and characterization of a human leptomeningeal cell line. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 30(3):475–483. [doi: 10.1002/jnr.490300304]
Muth, H., Kreis, I., Zimmermann, R., Tillmanns, H., Hölschermann, H., 2005. Differential gene expression in activated monocyte-derived macrophages following binding of factor VIIa to tissue factor. Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 94(5):1028–1034.
Nekludov, M., Antovic, J., Bredbacka, S., Blombäck, M., 2007. Coagulation abnormalities associated with severe isolated traumatic brain injury: cerebral arterio-venous differences in coagulation and inflammatory markers. Journal of Neurotrauma, 24(1):174–180. [doi:10.1089/neu.2006.0173]
Ogihara, K., Aoki, K., Zubkov, A.Y., Zhang, J.H., 2001. Oxyhemoglobin produces apoptosis and necrosis in cultured smooth muscle cells. Brain Research, 889(1–2):89–97. [doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(00)03120-6]
Pradilla, G., Wang, P.P., Legnani, F.G., 2004. Prevention of vasospasm by anti-CD11/CD18 monoclonal antibody therapy following subarachnoid hemorrhage in rabbits. Journal of Neurosurgery, 101(1):88–92. [doi:10.3171/jns. 2004.101.1.0088]
Prignano, F., 1998. Immunophenotype analysis of normal human dendritic cells isolated from epidermis and dermis. International Journal of Dermatology, 37(2):116–119. [doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.1998.00116.x]
Raymackers, J., Daniels, A., de Brabandere, V., Missiaen, C., Dauwe, M., Verhaert, P., Vanmechelen, E., 2000. Identification of two-dimensionally separated human cerebrospinal fluid proteins by N-terminal sequencing, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-mass spectrometry, nanoliquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-time of flight-mass spectrometry, and tandem mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis, 21(11):2266–2283. [doi:10. 1002/1522-2683(20000601)21:11<2266::AID-ELPS2266>3.0.CO;2-Z]
Recinos, P.F., Pradilla, G., Thai, Q.A., 2006. Controlled release of lipopolysaccharide in the subarachnoid space of rabbits induces chronic vasospasm in the absence of blood. Surgical Neurology, 66(5):463–469. [doi:10.1016/j.surneu.2006.04.010]
Sanchez, C.M., Suarez, M.A., Nebra, A., 2004. Early activation of coagulation and fibrinolysis in traumatic brain injury and spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a comparative study. Neurologia, 19(2):44–52.
Stein, S.C., Smith, D.H., 2004. Coagulapathy in traumatic brain injury. Neurocritical Care, 1(4):479–488. [doi:10. 1385/NCC:1:4:479]
Takizawa, T., Tada, T., Kitazawa, K., 2001. Inflammatory cytokine cascade released by leukocytes in cerebrospinal fluid after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurological Research, 23(7):724–730. [doi:10.1179/016164101101199 243]
Todo, K., Kitagawa, K., Sasaki, T., Omura-Matsuoka, E., Terasaki, Y., Oyama, N., Yagita, Y., Hori, M., 2008. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor enhances leptomeningeal collateral growth induced by common carotid artery occlusion. Stroke, 39(6):1875–1882. [doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.503433]
Wada, H., Hashimoto, K., Wada, Y., Kobayashi, M., Izumi, A., Sugiyama, A., Kohro, T., Hamakubo, T., Kodama, T., 2002. Extensive oligonucleotide microarray transcriptome analysis of the rat cerebral artery and arachnoid tissue. Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis, 9(5): 224–232.
Wang, L., Shi, J.X., Yin, H.X., 2005. The influence of subarachnoid hemorrhage on neurons: an animal model. Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Science, 35(1):79–85.
Zubkov, A.Y., Tibbs, R.E., Clower, B., 2002. Morphological changes of cerebral arteries in a canine double hemorrhage model. Neuroscience Letters, 326(2):137–143. [doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(02)00188-X]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30370497) and the Science and Technology Research Program of Zhejiang Province, China (No. 2007-C-33039)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xin, Zl., Wu, Xk., Xu, Jr. et al. Arachnoid cell involvement in the mechanism of coagulation-initiated inflammation in the subarachnoid space after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 11, 516–523 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000099
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000099
Key words
- Arachnoid cells
- Cell culture
- Human leukocyte antigen-DR (HLA-DR)
- Soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2r)