Abstract
Background: Rotational malalignment after intramedullary tibial nailing is rarely addressed in clinical studies.Malrotation (especially >10°)of the lower extremity can lead to development and progression of degenerative changes in knee and ankle joints. The purpose of this study is to determine the incidence and severity of tibial malrotation after reamed intramedullary nailing for closed diaphyseal tibial fractures.
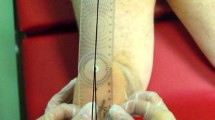
Materials and Methods: Sixty patients (53 males and 7 females) with tibial diaphyseal fracture were included in this study. The mean age of the patients was 33.4 ± 13.3 years. All fractures were manually reduced and fixed using reamed intramedullary nailing. A standard method using bilateral limited computerized tomography was used to measure the tibial torsion. A difference greater than 10° between two tibiae was defined as malrotation.
Results: Eighteen (30%) patients had malrotation of more than 10°. Malrotation was greater than 15° in seven cases. Good or excellent rotational reduction was achieved in 70% of the patients. There was no statistically significant relation between AO tibial fracture classification and fibular fixation and malrotation of greater than 10°.
Conclusions: Considering the high incidence rate of tibial malrotation following intramedullary nailing, we need a precise method to evaluate the torsion intraoperatively to prevent the problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lang GJ. Fractures of the tibial diaphysis. In: Kellam JF, editor. Orthopaedic Knowledge Update: Trauma. Rosemont, IL: AAOS; 2000. p. 177–89
Fortis AP, Dimas A, Lamprakis AA. Expandable nailing system for tibial shaft fractures. Injury 2008;39:940–6.
Weninger P, Tschabitscher M, Traxler H, Pfafl V, Hertz H. Intramedullary nailing of proximal tibia fractures–an anatomical study comparing three lateral starting points for nail insertion. Injury 2010;41:220–5.
Puloski S, Romano C, Buckley R, Powell J. Rotational malalignment of the tibia following reamed intramedullary nail fixation. J Orthop Trauma 2004;18:397–402.
Koo H, Hupel T, Zdero R, Tov A, Schemitsch EH. The effect of muscle contusion on cortical bone and muscle perfusion following reamed, intramedullary nailing: A novel canine tibia fracture model. J Orthop Surg Res 2010;5:89.
Buckley R, Mohanty K, Malish D. Lower limb malrotation following MIPO technique of distal femoral and proximal tibial fractures. Injury 2011;42:194–9.
Kahn KM, Beals RK. Malrotation after locked intramedullary tibial nailing: Three case reports and review of the literature. J Trauma 2002;53:549–52.
Jend HH, Heller M, Dallek M, Schoettle H. Measurement of tibial torsion by computer tomography. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1981;22:271–6.
Prasad CV, Khalid M, McCarthy P, O’Sullivan ME. CT assessment of torsion following locked intramedullary nailing of tibial fractures. Injury 1999;30:467–70.
Jakob RP, Haertel M, Stüssi E. Tibial torsion calculated by computerised tomography and compared to other methods of measurement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1980;62:238–42.
Hutter CG Jr, Scott W. Tibial torsion. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1949;31:511–8.
Clementz BG, Magnusson A. Fluoroscopic measurement of tibial torsion in adults. A comparison of three methods. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 1989;108:150–3.
Johner R, Wruhs O. Classification of tibial shaft fractures and correlation with results after rigid internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1983;178:7–25.
Eckhoff DG. Effect of limb malrotation on malalignment and osteoarthritis. Orthop Clin North Am 1994;25:405–14.
Turner MS. The association between tibial torsion and knee joint pathology. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1994;302:47–51.
Puno RM, Vaughan JJ, Stetten ML, Johnson JR. Long-term effects of tibial angular malunion on the knee and ankle joints. J Orthop Trauma 1991;5:247–54.
van der Schoot DK, Den Outer AJ, Bode PJ, Obermann WR, van Vugt AB. Degenerative changes at the knee and ankle related to malunion of tibial fractures. 15-year follow-up of 88 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1996;78:722–5.
Bonnevialle P, Andrieu S, Bellumore Y, Challé JJ, Rongières M, Mansat M. Torsional abnormalities and length discrepancies after intramedullary nailing for femoral and tibial diaphyseal fracture. Computerized tomography evaluation of 189 fractures. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 1998;84:397–410.
Velazco A, Fleming LL. Open fractures of the tibia treated by the Hoffmann external fixator. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1983;180:125–32.
Court-Brown CM, Christie J, McQueen MM. Closed intramedullary tibial nailing. Its use in closed and type I open fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1990;72:605–11.
Alho A, Ekeland A, Strømsøe K, Follerås G, Thoresen BO. Locked intramedullary nailing for displaced tibial shaft fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1990;72:805–9.
Williams J, Gibbons M, Trundle H, Murray D, Worlock P. Complications of nailing in closed tibial fractures. J Orthop Trauma 1995;9:476–81.
Krishan A, Peshin C, Singh D. Intramedullary nailing and plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal metaphyseal tibia and fibula. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 2009;17:317–20.
Freedman EL, Johnson EE. Radiographic analysis of tibial fracture malalignment following intramedullary nailing. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1995;315:25–33.
O’Dwyer KJ, Chakravarty RD, Esler CN. Intramedullary nailing technique and its effect on union rates of tibial shaft fractures. Injury 1994;25:461–4.
Pintore E, Maffulli N, Petricciuolo F. Interlocking nailing for fractures of the femur and tibia. Injury 1992;23:381–6.
Lambiris E, Tyllianakis M, Megas P, Panagiotopoulos E. Intramedullary nailing: Experience in 427 patients. Bull Hosp J Dis 1996;55:25–7.
Tu YK, Lin CH, Su JI, Hsu DT, Chen RJ. Unreamed interlocking nail versus external fixator for open type III tibia fractures. J Trauma 1995;39:361–7.
Krettek C, Schandelmaier P, Tscherne H. Nonreamed interlocking nailing of closed tibial fractures with severe soft tissue injury. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1995;315:34–47.
Sayli U, Bölükbasi S, Atik OS, Gündogdu S. Determination of tibial torsion by computed tomography. J Foot Ankle Surg 1994;33:144–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jafarinejad, A.E., Bakhshi, H., Haghnegahdar, M. et al. Malrotation following reamed intramedullary nailing of closed tibial fractures. IJOO 46, 312–316 (2012). https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.96395
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.96395